FTD-associated behavioural and transcriptomic abnormalities in ‘humanized’progranulin-deficient mice: A novel model for progranulin-associated FTD
 Potential key epigenetic players in COVID-19 infection
Potential key epigenetic players in COVID-19 infection
Abstract
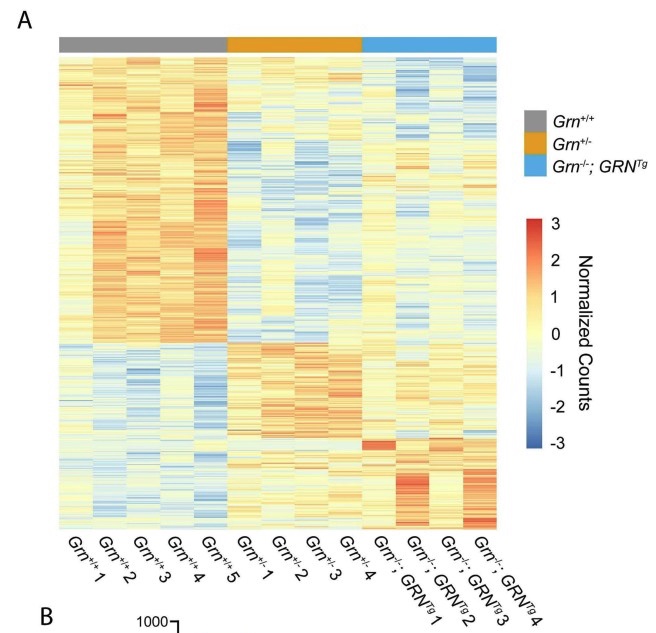
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is an early onset dementia characterized by neuropathology and behavioural changes. A common genetic cause of FTD is haploinsufficiency of the gene progranulin (GRN). Mouse models of progranulin deficiency have provided insight into progranulin neurobiology, but the description of phenotypes with preclinical relevance has been limited in the currently available heterozygous progranulin-null mice. The identification of robust and reproducible FTD-associated behavioural, neuropathological, and biochemical phenotypes in progranulin deficient mice is a critical step in the preclinical development of therapies for FTD. In this work, we report the generation of a novel, ‘humanized’ mouse model of progranulin deficiency that expresses a single, targeted copy of human GRN in the absence of mouse progranulin. We also report the in-depth, longitudinal characterization of humanized progranulin-deficient mice and heterozygous progranulin-null mice over 18 months. Our analysis yielded several novel progranulin-dependent physiological and behavioural phenotypes, including increased marble burying, open field hyperactivity, and thalamic microgliosis in both models. RNAseq analysis of cortical tissue revealed an overlapping profile of transcriptomic dysfunction. Further transcriptomic analysis offers new insights into progranulin neurobiology. In sum, we have identified several consistent phenotypes in two independent mouse models of progranulin deficiency that are expected to be useful endpoints in the development of therapies for progranulin-deficient FTD. Furthermore, the presence of the human progranulin gene in the humanized progranulin-deficient mice will expedite the development of clinically translatable gene therapy strategies.